Reliable & regulated
Licensed across multiple jurisdictions, ensuring transparency and security.
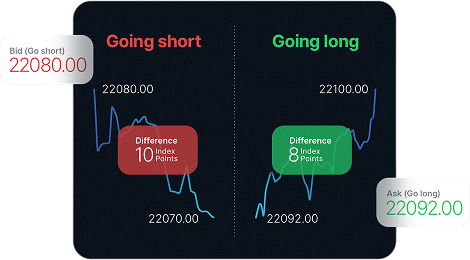
Cost-effective trading
Spreads as low as 0.0 pips, fast execution, and transparency.
Market expertise
Trade smarter with in-depth, real-time analysis from our research team.
Multilingual support
A dedicated multilingual Customer Support team available in your preferred language.
Intuitive platforms
Trade with confidence on industry-leading platforms available across all devices.
Portfolio diversity
10,000+ CFDs across Forex, Shares, Indices, Commodities, Bonds, ETFs, and Digital Currencies.